Understanding Gut Health
- What is Gut Health? Gut health refers to the state of balance and functionality within your digestive system, particularly the microbiome—a diverse community of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi living in your intestines. A healthy gut is crucial for proper digestion, absorption of nutrients, and protection against harmful pathogens.
- Why Is Gut Health Important? The gut does more than just digest food; it’s deeply connected to many aspects of your overall health. A balanced gut can lead to improved immunity, better mood and mental health, effective digestion, and even a lower risk of chronic diseases.
2. The Gut Microbiome: The Key to Your Health
- What is the Gut Microbiome? The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem of microorganisms that reside in your digestive tract. These microbes play an essential role in breaking down food, producing vitamins, and protecting against harmful bacteria.
- How the Gut Microbiome Affects Your Body A healthy microbiome supports digestion, immune function, and even mental health. Imbalances, such as a reduction in beneficial bacteria, can contribute to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), allergies, obesity, and depression.
3. The Connection Between Gut Health and Overall Well-Being

- Gut-Brain Axis: The Connection Between Gut and Mental Health The gut and brain are connected via the gut-brain axis, a communication network that links the emotional and cognitive centers of the brain with peripheral intestinal functions. This connection explains why an unhealthy gut can lead to mood disorders and stress.
- Immune System and Gut Health A significant portion of the immune system is located in the gut. A healthy gut can protect against infections and diseases by regulating the immune response and reducing inflammation.
4. Signs of an Unhealthy Gut
- Digestive Issues Symptoms like bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, and heartburn can indicate an imbalance in your gut microbiome.
- Frequent Infections and Weakened Immunity If you’re frequently getting sick, it could be a sign that your gut is not supporting your immune system effectively.
- Unexplained Mood Swings and Fatigue Since the gut produces a significant amount of the body’s serotonin (a key neurotransmitter for mood), an unhealthy gut may contribute to depression, anxiety, and fatigue.
5. How to Achieve and Maintain Optimal Gut Health

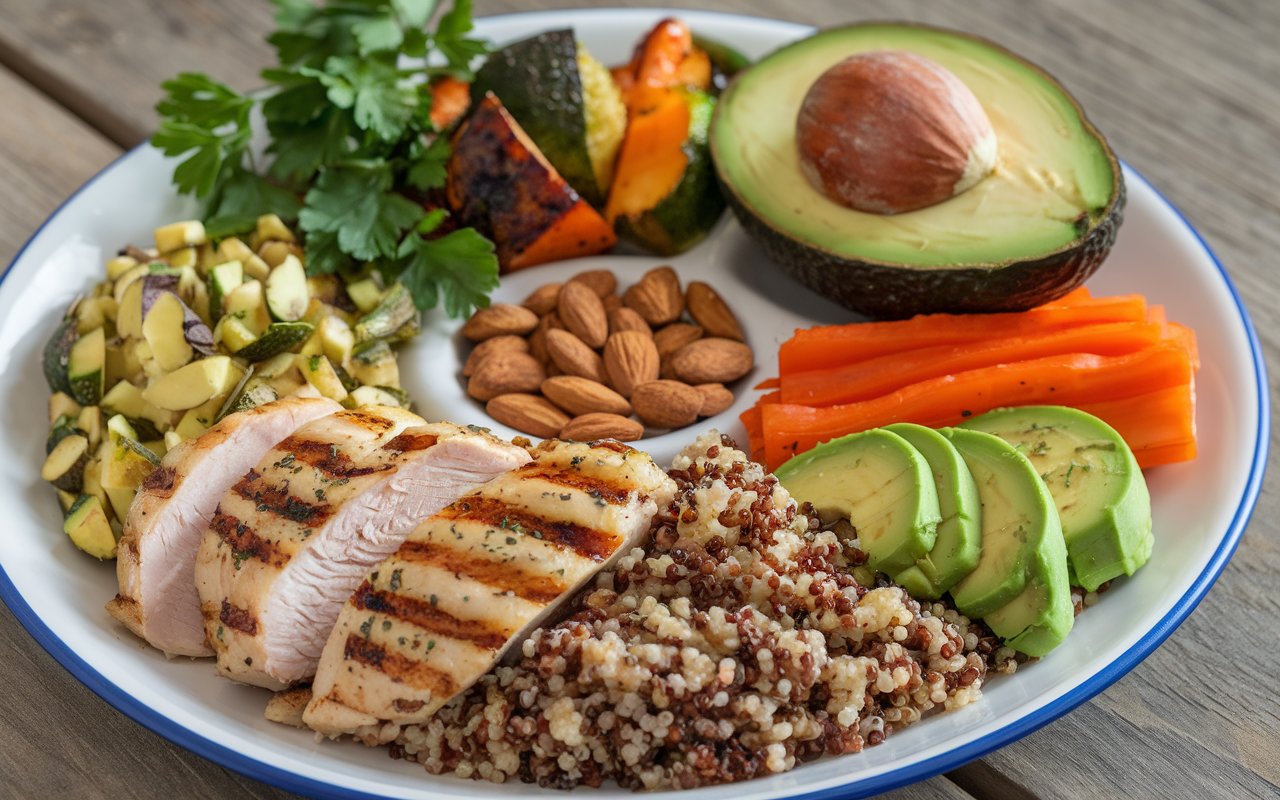
- Incorporate a Balanced Diet Eat Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber feeds the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes are excellent sources of dietary fiber. Include Probiotics and Prebiotics: Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria found in foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut. Prebiotics, found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas, are types of fiber that feed these good bacteria.
- Limit Processed Foods and Sugars Processed foods and sugars can disrupt the balance of bacteria in your gut, leading to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria. Reducing your intake of these foods can help maintain a healthy microbiome.
- Stay Hydrated Drinking plenty of water supports digestion and the absorption of nutrients, which is essential for a healthy gut.
- Manage Stress Chronic stress can negatively impact your gut health by disrupting the gut-brain axis. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and exercise can help reduce stress and promote gut health.
- Exercise Regularly Regular physical activity promotes healthy digestion and can help maintain a balanced microbiome.
6. Debunking Common Myths About Gut Health
- Myth 1: All Bacteria are Harmful Not all bacteria are bad. In fact, many bacteria in your gut are essential for good health. These beneficial bacteria aid in digestion, produce vitamins, and protect against harmful microbes.
- Myth 2: Probiotics Alone Can Fix Gut Issues While probiotics are beneficial, they are not a cure-all. Gut health requires a holistic approach, including a balanced diet, hydration, and stress management.
- Myth 3: Gut Health Only Affects Digestion Gut health impacts more than just digestion; it’s linked to your immune system, mental health, and overall well-being.
7. Steps to Restore Gut Balance if You’re Experiencing Issues
- Identify and Eliminate Food Triggers Common triggers like gluten, dairy, and processed foods can contribute to gut imbalance. An elimination diet can help identify specific foods that may be causing issues.
- Consider Supplementation In some cases, supplements like probiotics, digestive enzymes, and fiber may be necessary to support gut health. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Seek Professional Guidance If you’re experiencing chronic gut issues, consider working with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized advice and treatment.

8. Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Gut Health
- The Importance of Gut Health in Your Daily Life A healthy gut is foundational to your overall health. By paying attention to your gut health and making informed choices, you can improve not just your digestion, but your mood, energy levels, and immune function as well.
- Empowering Yourself with Knowledge and Action Understanding the importance of gut health and taking proactive steps to maintain it can lead to a healthier, happier life. Start with small changes, such as incorporating more fiber-rich foods into your diet and managing stress, and build from there




2 thoughts on “Unlocking the Secrets to Optimal Gut Health: Why It Matters and How to Achieve It”